Connecting a battery seems simple, but mixing up the terminals can lead to sparks, damage, and even injury. Understanding the difference between positive (+) and negative (-) terminals is crucial for safety and proper operation.
- Identifying Battery Terminals
- Why Polarity Matters
- Preventing Sparks and Damage
- Dealing with a Reversed Connection
- Specific Applications and Considerations
- Jump-Starting a Car
- Solar Power Systems
- Electronics Projects (DIY)
- Battery Chargers
- Tools for Checking Polarity
- Advanced Battery Systems
- Safety First!
- Final Thoughts
- Troubleshooting Common Polarity Issues
- The Device Doesn’t Turn On
- Sparks When Connecting
- Battery Overheating
- Staying Updated on Battery Technology
- Beyond Simple Batteries: Understanding Polarity in Complex Systems
- Power Supplies
- Photovoltaic (PV) Systems
- Electric Motors
- The Future of Battery Safety
Identifying Battery Terminals
Most batteries clearly mark the terminals. Look for these indicators:
- Positive (+): Often marked with a plus sign, red color, or the letters POS. The terminal is usually slightly larger than the negative terminal.
- Negative (-): Typically marked with a minus sign, black color, or the letters NEG.
If the markings are unclear, consult the battery’s documentation or the device’s manual.
Why Polarity Matters
Electrical devices are designed to work with current flowing in a specific direction. Reversing the polarity can cause:
- Short Circuits: A direct path for electricity to flow bypassing intended components, generating heat and sparks.
- Damage to Electronics: Sensitive components can be fried by reverse polarity.
- Battery Damage: Overheating or even explosion in rare cases.
- Fire Hazard: Sparks can ignite flammable materials.
Preventing Sparks and Damage
Follow these precautions to avoid polarity-related issues:
- Double-Check Polarity: Before connecting any battery, verify the positive and negative terminals on both the battery and the device.
- Match Colors: Red cables usually connect to the positive terminal, and black cables to the negative terminal.
- Use Correct Cables: Ensure the cables are the appropriate size and gauge for the application.
- Connect in the Correct Order: When jump-starting a car, connect the positive cables first, then the negative cable to a grounded metal part of the car frame (away from the battery).
- Disconnect in Reverse Order: When disconnecting, remove the negative cable first.
- Read the Manual: Always consult the device’s manual for specific instructions and warnings.
Dealing with a Reversed Connection
If you accidentally reverse the polarity:
- Immediately Disconnect: Remove the battery as quickly as possible.
- Inspect for Damage: Check the battery, device, and cables for signs of burning, melting, or other damage.
- Do Not Reconnect: Avoid reconnecting the battery until you have identified and addressed any damage.
- Consult a Professional: If you are unsure about the extent of the damage or how to proceed, seek help from a qualified technician.
Understanding and respecting battery polarity is essential for safety and preventing costly damage. By following these simple guidelines, you can avoid sparks, protect your electronics, and ensure the safe and reliable operation of your devices.
Specific Applications and Considerations
The principles of polarity apply across various applications, but here are some specific areas where understanding and careful connection are paramount:
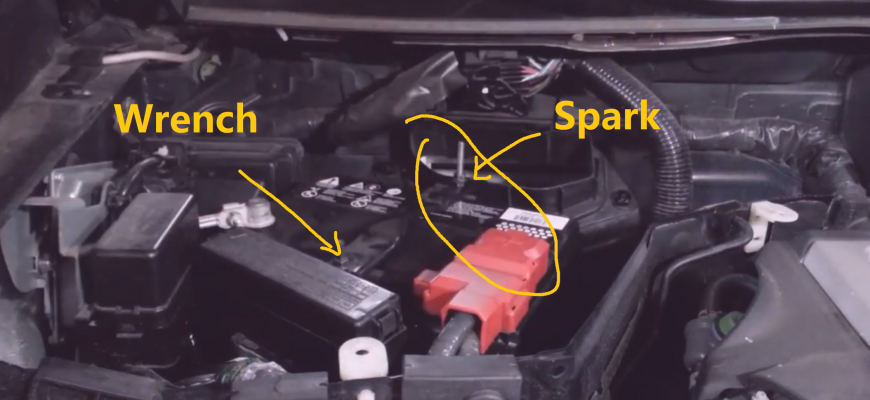
Jump-Starting a Car
Jump-starting a car is a common scenario where polarity mistakes can be dangerous. The correct procedure minimizes the risk of sparks near the battery, which could ignite hydrogen gas released during charging. Remember to:
- Connect the red (positive) cable to the positive terminal of the dead battery.
- Connect the other end of the red cable to the positive terminal of the good battery.
- Connect the black (negative) cable to the negative terminal of the good battery.
- Connect the final end of the black cable to a grounded, unpainted metal surface on the dead car’s frame, away from the battery. This is crucial!
Disconnect in the reverse order.
Solar Power Systems
Solar panels and charge controllers are sensitive to polarity. Reversing the connections can severely damage these components. Always double-check the wiring diagram and use a multimeter to verify the polarity before connecting anything.
Electronics Projects (DIY)
When working on electronics projects, breadboards, and circuits, pay close attention to the polarity of components like LEDs, diodes, and integrated circuits. Incorrect polarity can cause them to fail instantly.
Battery Chargers
Ensure the battery charger’s clips are correctly attached to the battery terminals. Most modern chargers have reverse polarity protection, but it’s always best to double-check.
Tools for Checking Polarity
While visual cues and markings are helpful, a multimeter provides a definitive way to determine polarity:
- Voltage Measurement: Set the multimeter to DC voltage mode. Connect the red probe to the potential positive terminal and the black probe to the potential negative terminal. If the reading is a positive voltage, your assumption is correct. If the reading is negative, the polarity is reversed.
- Continuity Test (with caution): In some cases, with a completely dead circuit, a continuity test can indirectly help identify polarity. However, avoid using continuity tests on powered circuits, as this can damage the multimeter or the circuit.
Advanced Battery Systems
For more complex battery systems, such as those found in electric vehicles or backup power systems, relying solely on visual cues is not enough. These systems often have sophisticated monitoring and protection circuits. Always refer to the manufacturer’s documentation and consult with qualified professionals for installation and maintenance.
Safety First!
Working with batteries involves electrical energy. Always prioritize safety:
- Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from potential sparks or acid splashes.
- Work in a well-ventilated area, especially when dealing with lead-acid batteries, which can release hydrogen gas.
- Avoid wearing metallic jewelry that could create a short circuit if it comes into contact with the terminals.
- Keep a fire extinguisher nearby, especially when working with large batteries or high-voltage systems.
Final Thoughts
A little knowledge and careful attention can prevent serious problems when working with batteries. By understanding the importance of polarity and following the guidelines outlined above, you can ensure safe and efficient operation of your electrical devices and systems.
Troubleshooting Common Polarity Issues
Even with the best precautions, mistakes can happen. Here’s how to troubleshoot some common polarity-related issues:
The Device Doesn’t Turn On
Possible Cause: Reversed polarity may have damaged the device’s fuse or internal circuitry.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check the fuse: Replace the fuse with one of the correct amperage.
- Inspect the device: Look for any signs of burning or damage to components.
- Consult a technician: If the fuse blows again immediately or if you see damage, seek professional help.
Sparks When Connecting
Possible Cause: Usually a direct short circuit due to reversed polarity or improper wiring.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Disconnect immediately: Remove the battery or power source.
- Inspect the wiring: Carefully check all connections for errors or damaged insulation.
- Use a multimeter: Test the circuit for shorts before reconnecting the power.
Battery Overheating
Possible Cause: Reversed polarity can cause a battery to charge in reverse or experience an internal short circuit, leading to overheating.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Disconnect the battery: Immediately remove the battery from the charger or device.
- Allow the battery to cool: Let the battery cool down completely before handling it.
- Dispose of the battery safely: A damaged battery should be disposed of properly according to local regulations. Do not attempt to recharge or reuse it.
Staying Updated on Battery Technology
Battery technology is constantly evolving. Staying informed about new battery types, charging methods, and safety precautions is crucial. Here are some resources:
- Manufacturer’s Websites: Check the websites of battery manufacturers for the latest product information and safety guidelines.
- Online Forums and Communities: Engage with online communities of electronics enthusiasts and professionals to share knowledge and learn from others’ experiences.
- Educational Websites: Explore websites dedicated to electronics and battery technology for in-depth articles and tutorials.
- Industry Publications: Subscribe to industry magazines and newsletters to stay up-to-date on the latest trends and developments.
Beyond Simple Batteries: Understanding Polarity in Complex Systems
The concept of polarity extends beyond simple battery connections and applies to more complex systems. For example:
Power Supplies
Power supplies convert AC voltage from the wall outlet to DC voltage needed by electronic devices. Understanding the polarity of the output voltage is crucial for connecting the power supply correctly.
Photovoltaic (PV) Systems
Solar panels generate DC electricity, and their polarity must be carefully considered when connecting them in series or parallel to create larger arrays. Incorrect polarity can damage the panels or the inverter.
Electric Motors
Reversing the polarity of the voltage applied to a DC motor will reverse its direction of rotation. This is a common technique used in robotics and other applications where directional control is required.
The Future of Battery Safety
Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving battery safety and reducing the risk of polarity-related accidents. Some of the areas of focus include:
- Smart Batteries: Batteries with built-in protection circuits that prevent reverse polarity connections.
- Improved Battery Management Systems (BMS): Advanced BMS systems that monitor battery voltage, current, and temperature to prevent overcharging, over-discharging, and other potentially dangerous conditions.
- Safer Battery Chemistries: Development of new battery chemistries that are less prone to thermal runaway and other safety hazards.
Mastering the fundamentals of battery polarity is an essential skill for anyone working with electronics. By understanding the risks associated with reversed polarity and following the best practices outlined in this article, you can prevent accidents, protect your equipment, and ensure the safe and reliable operation of your battery-powered devices. Remember to always double-check your connections, use appropriate tools and safety precautions, and stay informed about the latest battery technology. A little extra care can go a long way in preventing costly mistakes and ensuring your safety.








A must-read for anyone working with batteries. Clear and concise explanations. I learned something new!
Excellent overview of battery polarity and the potential consequences of incorrect connections.
This article is a lifesaver! I’ve almost made the mistake of reversing polarity before. Great advice.
Very informative! The section on preventing sparks and damage is particularly helpful. Thanks!
Excellent article! I always double-check polarity, but this is a great reminder of why it’s so important.
Simple, yet crucial information. I appreciate the clear explanation of the risks involved.
I like the practical advice on jump-starting a car. Very important to get the order right!
Concise and to the point. A great resource for anyone working with electronics.
Well-written and easy to understand. The tips on identifying terminals are very useful.