In the ever-evolving landscape of automotive technology, the accuracy and reliability of engine management systems hinge significantly on the performance of various sensors, particularly the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor. This critical component plays a vital role in optimizing engine performance and fuel efficiency. Therefore, understanding the best practices and techniques for testing MAP sensors is essential for automotive technicians and engineers alike. This article delves into the intricacies of MAP sensor testing, providing a comprehensive overview of effective methodologies and strategies.
- Understanding the MAP Sensor
- Testing Techniques for MAP Sensors
- 1. Visual Inspection
- 2. Voltage Testing
- 3. Pressure Testing
- 4. Scan Tool Diagnostics
- Best Practices for MAP Sensor Testing
- 1. Regular Maintenance Checks
- 2. Use Quality Replacement Parts
- 3. Document Findings
- 4. Continuous Education and Training
- Advanced Techniques in MAP Sensor Testing
- 5. Oscilloscope Analysis
- 6. Temperature and Environmental Considerations
- 7. Simulation of Engine Conditions
- Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- 1. Electrical Issues
- 2. Vacuum Leaks
- 3. Contamination
Understanding the MAP Sensor
The MAP sensor measures the pressure within the intake manifold, providing essential data to the engine control unit (ECU) to adjust fuel injection and ignition timing. A faulty MAP sensor can lead to a plethora of issues, including poor fuel economy, erratic engine performance, and increased emissions. Consequently, regular testing and maintenance of this sensor are paramount.
Testing Techniques for MAP Sensors
When it comes to testing MAP sensors, technicians can employ a variety of methods to ensure optimal functionality. Here are some widely accepted techniques:
1. Visual Inspection
- Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the MAP sensor and its wiring harness.
- Check for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion that could affect performance.
- Ensure that the vacuum lines connected to the sensor are intact and free from leaks.
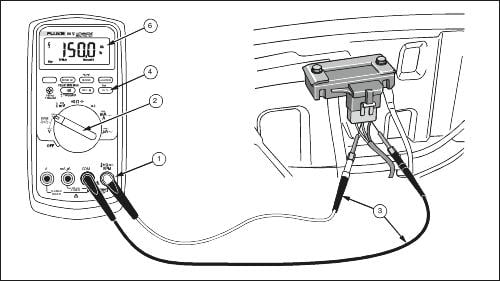
2. Voltage Testing
- Utilize a multimeter to measure the voltage output of the MAP sensor.
- With the ignition on (but the engine off), the voltage should typically be around 4.5 to 5 volts for a functioning sensor.
- As the engine runs, monitor the voltage changes in response to engine load; it should vary between 0.5 to 4.5 volts depending on the manifold pressure.
3. Pressure Testing
- For a more precise evaluation, a pressure gauge can be connected to the intake manifold.
- By comparing the gauge readings to the sensor’s output voltage, technicians can verify accuracy.
- Ensure that the readings correlate within the acceptable range specified by the manufacturer.
4. Scan Tool Diagnostics
- Utilize an OBD-II scan tool to read the MAP sensor data.
- Check for any stored trouble codes that may indicate issues with the MAP sensor or related systems.
- Analyze live data to assess the sensor’s response during various engine conditions.
Best Practices for MAP Sensor Testing
In addition to employing effective testing techniques, adhering to best practices can enhance the reliability and efficiency of MAP sensor diagnostics. Here are some recommendations:
1. Regular Maintenance Checks
- Incorporate MAP sensor testing into routine vehicle maintenance schedules.
- Address any identified issues promptly to prevent further engine complications.
2. Use Quality Replacement Parts
- When replacement is necessary, opt for high-quality OEM parts to ensure compatibility and performance.
- Inferior components can lead to recurrent sensor failures and misdiagnoses.
3. Document Findings
- Keep detailed records of testing procedures, findings, and any repairs performed.
- This documentation can aid in future diagnostics and provide valuable insights into recurring issues.
4. Continuous Education and Training
- Stay updated with the latest industry trends and advancements in sensor technology.
- Participate in training programs to refine testing skills and improve diagnostic accuracy.
The MAP sensor is a crucial element in modern automotive systems, influencing both performance and efficiency. By implementing effective testing techniques and adhering to best practices, automotive professionals can ensure that this component operates optimally, reducing the likelihood of engine-related issues. As technology continues to evolve, staying informed and skilled in MAP sensor diagnostics will be essential for maintaining the integrity of vehicle performance.
Advanced Techniques in MAP Sensor Testing
As automotive technology continues to advance, so too do the methods employed for testing components like the MAP sensor. Beyond basic diagnostics, several advanced techniques can provide deeper insights into sensor performance. These methods can help technicians pinpoint problems that might not be evident through standard testing.
5. Oscilloscope Analysis
- Using an oscilloscope allows for a detailed examination of the MAP sensor’s output waveform.
- By capturing the voltage signal in real-time, technicians can identify irregularities that might indicate sensor malfunction.
- Look for consistent wave patterns that correspond to engine load and RPM; deviations could signify issues.
6. Temperature and Environmental Considerations
- MAP sensors can be affected by extreme temperatures and environmental conditions.
- Testing the sensor across a range of temperatures can help determine its reliability and functionality in diverse conditions.
- Consider incorporating thermal imaging or temperature probes to assess sensor performance accurately.
7. Simulation of Engine Conditions
- Employing a controlled environment to simulate varying engine conditions can yield valuable data.
- Using a test bench setup, technicians can manipulate vacuum levels and pressure to observe how the MAP sensor responds.
- This method offers a clear picture of sensor behavior under different operational scenarios.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
When testing MAP sensors, several common issues may arise. Understanding these can aid technicians in troubleshooting effectively:
1. Electrical Issues
- Faulty wiring or poor connections can lead to inaccurate readings or complete sensor failure.
- Regularly inspect connectors for corrosion, dirt, or loose fittings that could disrupt electrical flow.
2. Vacuum Leaks
- A vacuum leak in the intake manifold can cause erratic MAP sensor readings.
- Utilize smoke tests or ultrasonic leak detectors to identify and rectify leaks.
3. Contamination
- Oil, dirt, and debris accumulation on the MAP sensor can affect its performance.
- Ensure that the sensor is clean and free from contaminants during inspections.
As vehicles become more complex, the role of the MAP sensor and the importance of rigorous testing techniques will only grow. Embracing advanced testing methods, understanding common issues, and adhering to best practices will empower technicians to maintain and enhance engine performance effectively. The future of automotive diagnostics lies in the hands of those who can adapt and innovate, ensuring that every component, including the MAP sensor, functions flawlessly for optimal vehicle performance;








I appreciate how this article emphasizes the importance of regular maintenance for the MAP sensor. It’s crucial for optimal engine performance!
The comprehensive overview of testing methodologies is impressive. This article will definitely help technicians improve their diagnostic skills.
Fantastic article! The breakdown of techniques makes it accessible for both new and experienced automotive professionals alike.
This article provides an excellent overview of MAP sensor testing techniques! The detailed explanations make it easy to understand the importance of each method.
Great insights into pressure testing! I never realized how vital it is for assessing MAP sensor functionality. Very informative read!
The visual inspection tips are spot on! It’s amazing how often issues can be identified just by looking closely at the components.
I found the section on voltage testing particularly useful. It’s great to have clear guidelines on what readings to expect from a functioning MAP sensor.